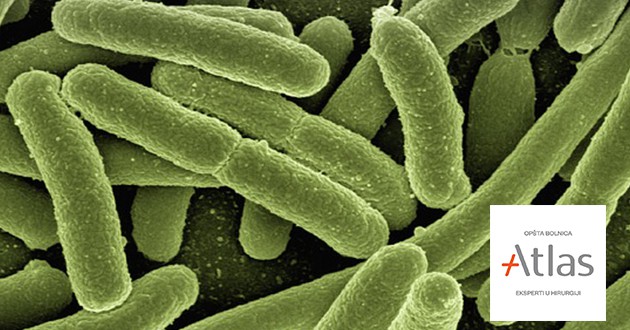
Escherichia coli is a type of bacterium that normally lives in the gut. Most types of E. coli are harmless and even help keep your digestive tract healthy. But some strains of this bacterium can cause diarrhea if you eat contaminated food or drink contaminated water.
While many of us associate Escherichia coli with food poisoning, it should be remembered that you can also get pneumonia, intestinal infection, and urinary tract infection with this infection. In fact, as many as 75% to 95% of urinary tract infections are caused by Escherichia coli.
Some versions of E. coli make you sick by making a toxin called Shiga in an infected organism. This toxin damages the intestinal mucosa. Escherichia coli strains producing this toxin are sometimes referred to as STEC, which is abbreviated as “E. coli producing Shiga toxin” (Shiga toxin-producing E. coli).
There is one particularly bad strain of Escherichia coli, O157: H7, that can really make you sick.
It causes abdominal cramps, vomiting and bloody diarrhea. It is a leading cause of acute kidney failure in children. It can also cause life-threatening symptoms such as fever, bleeding, confusion and other…
Causes of Escherichia coli infection
It is very easy to get infected with Escherichia coli if you bring in even a small amount of it into your body. Among the different ways of infections, these are some:
- Minced meat: if you eat minced meat carrying Escherichia coli and the meat is not enough boiled to kill bacteria. When the meat is processed, sometimes bacteria from the gut animals enter meat. This is more the case with minced meat.
- Raw milk: if you drink unpasteurized milk that is not boiled bacteria. Collie escherichia can enter milk from the udder of the cow or from milking equipment.
- Vegetables and fruits: You can eat fresh vegetables or fruits that are contaminated with water that has these bacteria. This happens most often when the fertilizer from surrounding animals mixes with water supply.
- Other foods and drinks: You can also get E. coli from non-pasteurized fruit juices and yogurt and cheese made from raw milk.
- Water: If you swallow water containing Escherichia coli, perhaps while swimming in a pool, lake or the pond.
- Other people: You can get E. coli from another person who has this bacterium.
- Colitis escheria can infect the urogenital tract if it is transferred from the intestinal tract, where it is normally found, due to inadequate use of the toilet.
As with most infectious diseases, the low immunity contributes to the onset and worsening of the disease infections itself.
Symptoms of Escherichia coli infection
You will probably start to feel sick 2 to 5 days after being infected with the bacterium
Escherichia coli. The most common symptoms of this type of infection are:
- Abdominal cramps
- Diarrhea, with blood admixtures
- Nausea
- Constant fatigue
- The elevated temperature may not be present, if it is – it may be insignificant.
In the case of urinary infection with Escherichia coli, the symptoms are usually wheezing at
urination, frequent urination, pain when urinating, urinary urgency and the like.
Most people who become infected with E. coli usually feel better within a week of the first symptoms. But some people have a serious complication called hemolytic uremic syndrome, which affects the kidneys. This is more likely to happen to the elderly and children.
Escherichia coli-treatment
The only way to determine for sure if you have an Escherichia coli infection is to send a sample of your stool or urine for laboratory analysis.
Fortunately, the gut infection with this bacterium usually goes away on its own.
In some types of Escherichia coli associated with diarrhea, such as waterborne diarrhea, antibiotics can shorten the duration of symptoms and can be used in moderately severe cases.
But if you have fever or bloody diarrhea, or if your doctor suspects E. coli that produces Shiga toxin, you should not take antibiotics. They can actually increase production of
Shiga toxins and worsen your symptoms.
It is important for you to rest and take plenty of fluids to replace what your body is losing through vomiting or diarrhea.
When you start to feel better, it is important that you first stick to a low-fiber diet, such as:
- crackers
- Tosted bread
- eggs
- rice
Dairy products and foods high in fat or fiber can aggravate your symptoms.
Natural treatment of urinary infection caused by Escherichia coli
It happens that some strains of Escherichia coli are resistant to antibiotics and it make the urinary tract infection more difficult to treat. Therefore, appropriate natural remedies may be included in the treatment of this infection. Well, to list the most effective:
Wild oregano oil has strong antimicrobial properties and contains carvacrol, an active ingredient that is effective in treating drug-resistant Escherichia coli.
Urinary infections are also aided by teas with antimicrobial activity, such as cranberry tea, parsley tea, twisted tea and the like. Cranberry juice is also effective in this case.
It will also help if you consume raw garlic, which is a natural antibiotic.
Probiotics (yogurt, kefir) and vitamin C (either as a supplement or in foods such as citrus) can help in the natural treatment of Escherichia coli.
Note
If you ever suspect that you are infected with Escherichia, you should first do appropriate diagnostic tests, and be sure to consult before starting any therapy with a doctor.
At the Atlas General Hospital you can do all the necessary examinations and laboratory analyzes in a short time, so feel free to call the call center phone and make your appointment: +381 11 785 88 88.