Gallstones are solid, stone-like lumps that form inside the gallbladder.
A stone can form in the gallbladder if there is a change or imbalance in the composition of the bile, or if the gallbladder is not completely emptied.
The presence of gallstones in the gallbladder is one of the most common diseases of the gallbladder, which often leads to inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis). Gallbladder inflammation is a condition that is most often resolved surgically, and surgical removal of the gallbladder is today the most common operation in the world (more often than appendicitis or hernia surgery).
What stones are in the gallbladder?
Gallstones can be very small, or the size of the gallbladder itself. It is generally less than 2.5 cm. Gallstones in 85% of cases consist of cholesterol, and in a smaller number of cases they can also be pigmented stones. The type of gallstones is very important because cholesterol stones will most likely respond to non-surgical treatment compared to pigment ones.
Gallstones (cholelithiasis) are diagnosed every year in a large number of people, and a large number of patients who already suffer from this disorder have been noted. Fortunately, most patients with gallstones do not show symptoms and do not need treatment.

Are gallstones dangerous?
In other cases, gallstones cause pain and must be treated: removal of either stones or gallbladder.
The mere presence of gallstones is not dangerous, but there are dangerous complications that can occur. These are inflammation of the bile ducts, gangrenous cholecystitis, jaundice, inflammation of the pancreas, sepsis, fistula (ileus).
In most cases, when there is no inflammation, gallstones do not give any symptoms, and when symptoms do occur, they are most often in the form of lumbar pain below the right costal arch with spreading to the back often a few hours after a heavy or fatty meal, nausea, vomiting and fever.
People who have gallstones can also have them in the bile ducts, and this condition is called choledocholithiasis.
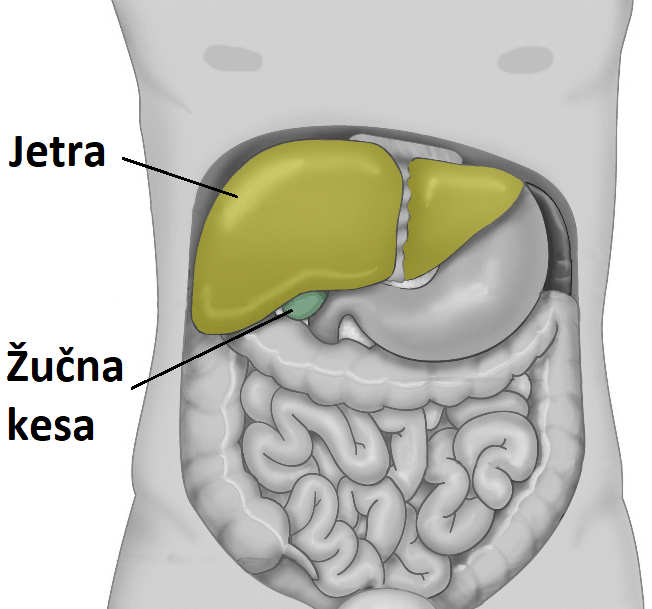
Where is Gallbladder located?
The gallbladder is located in the upper right part of the stomach, below the liver. The gallbladder is a plum-shaped muscular organ, 1.2 to 2.4 cm long, located in the upper right part of the abdomen, below the liver. It is connected to the liver and intestines through small tubes called ducts.
What does the gallbladder do?
The main purpose of the gallbladder is to concentrate and collect bile, a greenish-brown fluid produced by the liver. Bile is needed for digestion and absorption of fatty foods, as well as for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Between meals, the gallbladder is relaxed and is affected by bile, where it is then stored and concentrated. During meals, fatty foods in the small intestine trigger the secretion of hormones (cholecystokinin), which stimulate gallbladder contractions. The gallbladder is partially emptied into the upper part of the small intestine (also called the duodenum). Here, bile helps in digestion and absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins. A few hours later, the gallbladder relaxes and begins to collect bile again.
Symptoms of gallstones
1.No symptoms (in 80 percent of cases)
Painless gallstones – Most people who have gallstones show no symptoms; their stones remain “quiet.” Silent gallstones are often detected by ultrasound or a CT scan taken for other reasons. Silent stones do not need to be treated, and the first symptoms of gallstones are usually mild.
2.Pain below the right costal arch
Bile Colic – Bile colic, also known as bile pain or biliary pain, is the most common symptom of gallstone disease. They are characterized by attacks of abdominal pain, often located below the upper abdomen, just below the ribs. You may also experience back pain in your right shoulder, nausea and vomiting. Bile colic is usually caused by the contraction of the gallbladder after a fatty meal. These contractions put pressure on the stones, which block the opening. The pain passes with the relaxation of the gallbladder after a few hours.
After the first attack of pain due to biliary colic, there is a high chance that you will have more severe symptoms in the future.
3.Lumbar abdominal pain with spreading to the back
4.Pain in the middle or right upper abdomen
5.Nausea
6.Vomiting
7.Elevated temperature
8.Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Complications caused by gallstones
Acute gallbladder inflammation (acute calculous cholecystitis) – means inflammation of the gallbladder. It occurs due to a total blockage of the gallbladder caused by repeated episodes of biliary colic. Unlike biliary colic, which disappears after a few hours, in the case of acute cholecystitis, the pain is constant, and the appearance of fever is common.
Acute cholecystitis is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention and hospital treatment. Treatment includes intravenous fluids, painkillers and, sometimes, antibiotics. Surgical removal of the gallbladder is recommended during or shortly after hospitalization. If left untreated, acute cholecystitis can lead to gallbladder rupture, a life-threatening condition.
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder (chronic calculous cholecystitis) occurs due to occasional obstruction of the gallbladder duct, after which acute inflammation occurs. When the concretion returns to the gallbladder, the inflammation subsides.
Complications can occur if the stone in the bile moves and blocks the part where the bile comes out (a condition called choledocholithiasis).
Acute cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts that causes pain, shivering and fever. Immediate treatment is necessary and usually means the removal of gallstones by a non-surgical method known as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography- ERCP.
Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas, associated with severe abdominal pain.
How to diagnose gallstones
- Examination by general practitioners, gastroenterologists and surgeons
- Laboratory analyzes: CBC with leukocyte formula
- Biochemical blood tests: isolated or conjugated bilirubin, gamma GT, AST, ALT etc.
- Urine analysis (urobilinogen and other analysis)
- Abdominal ultrasound
- X-ray of the abdomen
- ERCP
- Laparoscopic exploration
Treatment of gallstones
Non-surgical treatment of gallstones:
1.Drugs (antispasmodics, anticholinergics, antibiotics)
2.ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) – removal of gallstones from the bile ducts
Surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy):
-Open cholecystectomy (gallbladder surgery)
-Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (laparoscopic gallbladder surgery): Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed instead of the classic operative incision of about 15-20 cm through 3 of 4 millimeter incisions, without cutting the structures of the anterior abdominal wall. Recovery is faster and all risks are smaller.
At the Atlas General Hospital within the Center for General Surgery, a team of doctors performs laparoscopic gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy) at a promotional price.
The cost of gallbladder surgery is 124,000 rsd and there are no hidden costs. The price includes all costs: surgical preparation, surgery and hospital day.

Is it possible to live without a gallbladder?
You can live without a gallbladder. By removing the gallbladder, complications such as perforation are prevented, when it ruptures and all the contents from it are poured into the inside of the abdominal cavity, which leads to an acute abdomen, which is an urgent condition.
There is also the possibility of clogging the pancreatic duct with stones and thus leading to acute pancreatitis (then pancreatic enzymes cannot be secreted into the intestines to aid digestion, but act on the pancreas itself leading to inflammation which is another emergency).
Both of these conditions are life-threatening, so gallbladder diseases should be taken seriously and its treatment should not be neglected.
Risk factors for gallstone formation
- Gender – Gallstones are more common in women
- Obesity
- Frequent fasting
- Chronic diseases (diabetes, cirrhosis of liver, Crohn’s disease and others)
- Hereditary factor
- Diet rich in saturated fats and refined sugars
- Pregnancy
- Oral hormone therapy (oral contraceptives and replacement therapy)
- Sudden weight loss (including patients who have undergone surgical treatment for weight loss
- Lack of physical activity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Sickle cell disease (and other conditions associated with the rapid destruction of red blood cells, for example in patients with mechanical heart valves)
- Cirrhosis of the liver or liver with a lot of scar tissue
- Age – The risk of gallstones increases as a person gets older. This condition is extremely rare in children and becomes more common over time, especially in people over the age of 40.
- Some medications
Call our call center on 0117858888 or 0603292411 for all questions regarding treatment and gallbladder surgery.
