Hyaluronic acid is a substance similar to a gel that is naturally present throughout the human body. In the joints, natural hyaluronic acid has several functions, including:
- Lubrication
Hyaluronic acid binds well to water, creating a viscous gel-like consistency. This viscous liquid provides lubrication and also acts as a shock absorber in the compound.
- Growth of cartilage and bones.
Hyaluronic acid helps in the growth and development of cartilage and bone joints by promoting the growth of new cells and tissues.
- Reducing inflammation.
Hyaluronic acid plays an important role in reducing joint inflammation and pain caused by injuries or tissue degeneration.
In the joints and in the rest of the body, hyaluronic acid also acts as a moisturizing cream, keeping the tissues hydrated. The highest concentrations of hyaluronic acid are found in the joints and eyeballs, where they help protect the eye lenses.
Use of hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is used for various treatments, such as those for joints, skin and eyes.
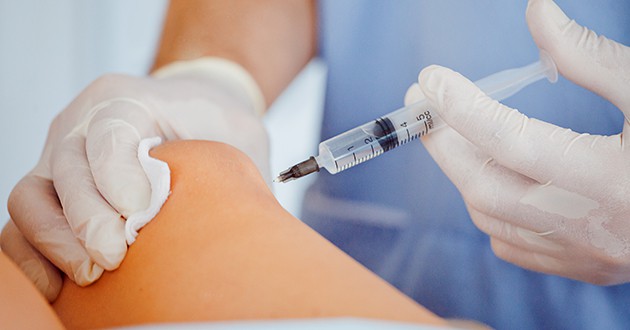
Hyaluronic acid injections are used to treat joints. These injections can be intraarticular (inside the joint capsule) or periarticular (around the joint capsule). Several joint diseases treated with hyaluronic acid include:
- Osteoarthritis
Hyaluronic acid injections can reduce or relieve inflammation caused by cartilage and bone wear in osteoarthritic joints. The injected gel helps restore lubrication and also causes the growth of new cartilage and bone tissue in these joints. Osteoarthritis of the knee, shoulder, ankle, hip and thumb can be treated with injections of hyaluronic acid.
- Frozen shoulder.
Injections of hyaluronic acid can help relieve stiffness in a frozen shoulder. Research has shown that reduced stiffness may be due to the effects of hyaluronic acid on reducing inflammation and islets in the synovial membrane. - Rheumatoid arthritis.
A recent small study found that injections of hyaluronic acid can help control inflammation and synovitis in the joints of the feet and caused by rheumatoid arthritis. - Ankle sprain.
Injection of hyaluronic acid into ankle sprain can help reduce inflammation and reduce pain. - Tennis elbow.
Chronic degeneration of the lateral tendon of the epoicondyle causing the tennis elbow can be treated by injection of hyaluronic acid into the elbow joint.
The use of hyaluronic acid injections is not recommended for children, women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, or in those who have a treatment site infection or a known allergy to hyaluronic acid. Treatment with hyaluronic acid is also not recommended for people with cancer or a history of cancer. Doctors cant predict who will benefit from hyaluronic acid injections. But many doctors give them to people with osteoarthritis of the knee whose symptoms do not improve with painkillers. Hyaluronic injections are often given to people who cannot take painkillers such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen sodium or who are unable (or are not ready) cfor omplete knee replacement surgery. Depending on the type your doctor uses, you may get one injection. Or you will get three to five injections at intervals of several weeks.
The injection is given in the same way for all species. First, the doctor cleans the area. If your knee is swollen from excess fluid, your doctor may inject a local painkiller, then insert the needle into your wrist to draw in excess fluid. While the same needle is still in place, the doctor can usually inject hyaluronic acid into the knee joint. After the injection, you should not do heavy activities for one or two days. Otherwise, you could resume normal activities.
Side effects
The most common short-term side effects are less pain at the injection site and less joint fluid accumulation. They disappear within a few days. Rarely, larger inflammation may occur in the injected joint.