The foot consists of 26 bones, more than 30 joints and a great number of ligaments, nerves and blood vessels.
The weight that foot bears when walking is twice or three times bigger than body weight, while during running it increases by 4 to 10 times, and according to science not a single artificial structure would be able to withstand such an effort.
If the foot, apart from locomotion and bearing multiple body weight is exposed to inadequate footwear which inhibits natural locomotion, it will result in callus formation, pain and acquired deformities.
How is this procedure carried out?
In the Atlas General Hospital patients are offered surgical, conservative and aesthetic foot treatments which solve the following problems and anomalies:
– bunions – limited movement of the big toe joint, “Hammer” fingers and ” claw” fingers, valgus, deformity of small toes (“windswept toes”), bunion ( digitus quintus varus) -metatarsalgia, uneven toes, heel pain, ingrown nails (unguis incamatus), ganglia, neuroms, pressed nerves, ankle and foot bones, “football ankle”, ankle instability, accident consequences.
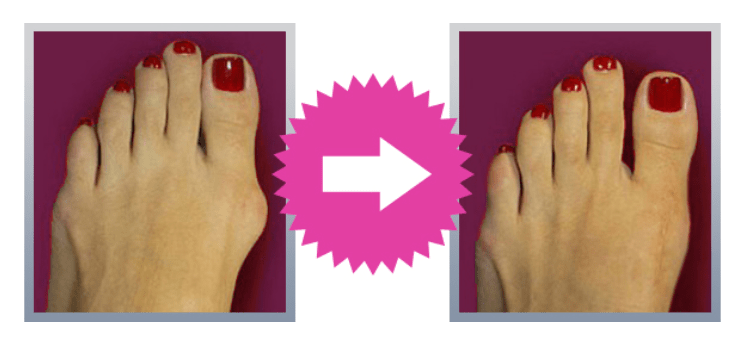
“Hammer toe”- Hallux valgus
Hammer toe is the bony deformity that is created in lower joint of toe. With time joint of the toe can become enlarged and painful, which sometimes can create difficulty while doing exercises or while walking. Hallux valgus or hammer toe is most request deformity of the foot disorder (and some dates are listing it as the most frequent of musculoskeletal system). It is considered that wearing narrow shoes with high heels is one of the most frequent causes of hammer toe, and is no wonder that it occurs most frequently (80%) in women around forty. It is also very important hereditary component because 60% of the patients with hallux valgus have one member of the family with the same deformity.
Clinical picture is pain because of the pressure of the shoes on pseudo exostosis and inflammation of the bursa that is caused by that irritation. Patients complain on pains in the metatarsal area (metatarsal transfer) transfer metatarsalgia, and in advanced cases there are secondary deformities of the rest of the toes, or secondary degenerative changes in middle part of the foot.
The most important diagnostic procedure is X ray of both feet in standing position (so called bifocal X ray picture). Pulling lines in the middle of I and II metatarsal bone and proximal phalanx we determine the angles how we estimate the degree of deformity, or we make the decision about the treatment.
Insoles and shoes made with your own measures cannot correct nor prevent progression of the deformity. Operation of hammer toe is the only solution.
We decide to operate hammer toe in case of intensive pain and inability to wear shoes. We choose the type of intervention relative to degree of deformity having in mind the degrees that we mentioned. For milder deformities today it is performed more often Chevron osteotomy, and in more advanced deformities it is more often performed so called Scarf osteotomy.
Postoperative rehabilitation after hallux valgus surgery includes crutch walking in post operative shoe in duration of 10-14 days. After stitches are removed, and during 4 to 6 weeks of bone healing, patient will be able to have full support on the heel. Returning to activities and wearing normal shoes after 6 to 8 weeks after the intervention.
Hammer toe
Hammer toe deformity causes toes to be bend downward instead of pointing forward. This type of deformity can effect any toe, but most often we find it on second and third toe.
Even though hammer toe can be present at birth, most often this deformity is developed during the time because of the arthritis or non adequate narrow shoes and high heels.

Risk factors of developing a hammer toe are:
- positive family anamnesis
- constant wearing of tight, narrow shoes
- presence of calluses, bunions in the feet region that are in reality thickened skin
How hammer toe is diagnosed?
Most often it is enough to perform clinical orthopedic examination with eventually X ray in two directions (AP, LAT).
Treatment for a hammer toe
Milder cases of a hammer toe where deformity is still reversible and can be treated with changing of shoes and adequate orthopedic insoles. More difficult cases with already irreversible deformity can be treated only surgically. The operation itself is safe for the patient and mostly patient is dismissed from the hospital on the same operating day.
Claw toes
Claw foot or claw toes are the same entity in diseases of the foot. It is a condition where toes are inward in form of animal claw.
It is a condition where toes are banded in form of animal claw. The condition is often seen on birth, or can be acquired during life. The deformity is not dangerous but is not comfortable for the patient. The diseases itself can point at some more important medical conditions as cerebral palsy or diabetes.
If you notice this type of foot please contact your orthopedic surgeon so that condition of foot would not deteriorate.
Symptoms of claw toes
Sometimes can be asymptomatic, joints of toes on feet that are closer to ankle are banded upward, while toes that are further from ankle are curled downwards. After some period with shoe contact wounds and calluses on toes are formed.
- Causes of formation
- Surgery in region of an ankle
- Injury of nerves in foot region
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Diabetes
- Cerebral palsy
- Stroke
How claw toes are treated?
Flexible deformities are treated with orthosis, taping, or gypsum (plaster) immobilization in some cases. In more difficult, non flexible deformities, surgery is the only solution.
Wind-swept toes deformity
Valgus deformity on the foot always remind us on hammer toe or in most of the cases it is the most often deformity that can be seen. As halux valgus or hammer toe do not represent isolated deformity especially when it is long lasting problem, there is foot valgization, or outward movements of other toes of the foot, all but big toe.
Windswept toes is always combined with hallux valgus, and only reasonable solution is surgical treatment.
Metatarsalgia – digitus quintus varus
Metatarsalgia is a condition when small joints of the feet become painful and inflamed.
Symptoms of metatarsalgia can include:
- Sharp pain or burning sensation in tarsometatarsal joints
- Pain becomes more intense during walking or running, and is decreasing during rest
- Sharp pain and tingling in toes
- Sensation of pins and needles in shoes
Causes for metatarsalgia formation:
- Intensive training, especially running
- Special type of foot
- Foot deformities
- Increased body weight
- Non adequate footwear
- Stress fracture
- Morton’s neuroma
Treatment of metatarsalgia is almost exclusively non surgical. Physical therapy, cryotherapy and right insole is obligatory.
Brachimetatarsia
This condition is most often congenital, although it can be acquired. Mostly one finger on foot is shorter then other, although more toes can be caught. Most often is caught fourth toe.
Treatment of Brachimetatarsia
If condition is asymptomatic and exclusively aesthetic there is no need to be treated. If there is constant pain in foot, treatment is exclusively surgical.
Heel pain, heel thorn (calcar calcanei), plantar fasciitis
Heel pain is one of most often reasons why patients come to see an orthopedic surgeon. There are some theories why the pain occurs in people that are inactive, that are sitting for a long periods of time or in athletes, or in people that are standing for prolonged period of time.
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis
- Pain in heel region and from the bottom of the feet
- The most intensive pain is in the morning and is calming during the day, but it never ceases
Treatment of heel pain
Treatment is mostly non operative: physical therapy, cryo therapy, an adequate orthotic insoles, exercises for stretching of plantar fascia.
In cases when there is no improvement, which is very rare, surgical treatment is considered.
Ingrown toenail (unguis incarnatus)
Ingrown toenail, also known as onychocryptosis or unguis incarnatus, is painful condition of the foot. That is happening when sharp pain of the nail is ingrowing in the skin on the edge of the toe. Ingrowth can occur on any nail, but is most often seen on big toe. First, there is pain and inflammation on the spot where nail is banded toward skin, and later on that inflammed region there is tissue that grows with drainage of yellowish secretion. Ingrown nails are more common in men than in women. Young people in their twenties and thirties are most commonly at risk.
Left untreated, ingrown nail can cause infection. Osteomyelitis is rare infection of the legs where bones are infected.
Causes of ingrown nails:
- Wearing shoes that are too tight or high heels
- Improper nail trimming (they should be cut straight, not under angle)
- Fungal infections of nails can cause thickening and widening of nail
- Acute injuries close to the nail or something that causes nail injuries (like football)
- If family member has similar problem of an ingrown nail, there is great possibility that you will have this problem also
- In some people nails are naturally curved or bone underneath can be “lifted”, and it raises possibility for possibility for development of ingrown nails
Neuroma
Neuroma is thickening of nerve tissue and can be seen on any nerve structure, as well as on the foot. When neuroma is on the foot it is most often seen as Morton’s neuroma (intermetatarsal neuroma) that is most often seen between third and fourth toe.
What causes a neuroma?
Any long nerve compression and irritation causes inflammation and formation of neuroma. The most often cause is tight shoes and high heels where compression is greatest on the front foot. In persons with bunions, flat or more flexible feet, there is increased risk for neuroma formation.
Neuroma’s symptoms
Pain and burning sensation, local numbness, sensation that there is something present in the shoe or sock during walk.
Diagnosis of neuroma
Clinical examination is most important as well as anamnestic data. Usually it is done MRI and CT as additional diagnosis.
Treatment of neuroma
When neuromas are dignosed in time non operative treatment gives good result: cryotherapy, physical therapy, orthotic insoles, shoe correction, NSAID, local cortico preparation. In patients where symptomatology is still present, surgical intervention of excision of damaged nerve is performed.
Hallux rigidus
Hallux rigidus, literally rigid big toe is often accompanied with pain and limited banding of toe upward, with possibility of banding big toe downward. In base of this clinical entity there are degenerative changes in region of basal (first metatarsophalangeal) toe joint.
Primary or juvenile hallux rigidus occurs in younger persons, as a rule due to disorder of head and metatarsal bone, and in the form of aseptic necrosis or osteochondritis dissecans. Secondary or adult hallux rigidus is multifactory genesis, and degenerative changes are dominant.
During examination usually we can see exostosis with dorsal side of basal joint. Big toe is usually stretched, dorsal flexion is extremely diminished while plantar is preserved. Diagnosis is confirmed with X ray that shows classic signs of ostheoartitis: joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, and osteophytes (especially dorsal). Treatment is conservative, and one effective measure is appropriate shoes that diminishes painful dorsiflexion.
In case of progression of the pain, most often surgical procedures are removing of dorsal osteophyte and dorsal edge of metatarsal bone and artrodesis of basal joint of the big toe.
“Football” joint
This kind of injury is often seen in professional footballs players, although it can be seen in other athletes and during recreational activities. It is impingement between tendons, ligaments and bones that build high ankle, tibia and talus.
It is created after repeated ball kicking movement when foot and ankle joint is under ultimate amplitudes and then it is constant contact between tibia and talus. With time on the edge of the bone calcification is created and new formed bone begins to bother and hurt.
Treatment of “football joint”
Non operative treatment is practically physical therapy and injection of local corticosteroid preparation, but it is necessary that those growths are removed surgically on both bones so that patient could be relieved.
Cause of ankle instability
Instability of the ankle is relatively common pathology in all professional and recreational athlets. Joint itself except tibia bones and talus are stabilized by lateral inner and outer ligaments, as well as ligaments between bones of under knee, tibia and fibula. In injuries in this soft tissue structures joint becomes unstable and sprains are often seen.
Reason for ankle instability
- Repeating of distortion, sprained ankle that are not adequately treated
- Fractures of joint
- Certain neurological disorders
Symptoms of ankle instability
Pain in the ankle, feeling of instability and inability to put any weight on it and changing direction and during walking, running on uneven terrain.
Diagnostic
Clinical examination and anamnesis are crucial in diagnostic in this injuries. Additional diagnosis are X ray and MRI.
Treatment of the ankle instability
Non operative treatment is performed in form of wearing orthosis and bandaging of the ankle.
Operative treatment is the only solution in professional athletes as well as young patients that are active sportively and in patients that do not tolerate orthosis.
A ganglion cyst
Ganglion cysts are tumefactions that are filled with gelatin liquid. They are formed mainly around tendon peritendium and joint capsule. Ganglion means node and is benign subcutaneous tumor. Most often it is found on the hand, and after that on the foot.Cause
It is still not clear why ganglion is formed, but it is assumed that previously there must be some kind of trauma or repeated microtrauma on the place of the formation.
Symptoms of ganglion
- Usually it is painless growth
- It can cause burning sensation or uneasiness if ganglion is in contact with the nerve
- Dull pain, if cyst makes pressure on the tendon or is in contact with the ankle
- Difficulty wearing shoes for the same irritation of the skin on the spot of the ganglion
Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be made with clinical examination regarding the fact that the change is visible with naked eye. There is possibility that additional diagnostic is made – X ray and MRI.
Treatment
Treatment is mainly non operative, monitoring of the cyst, modification of the shoes. In case when problems persist, aspiration of the cyst is done and excisional surgery.
Pinched nerves
Pinched nerve or nerve compression can be caused by different reasons. Regarding the fact that nerves go through narrow channels and peritendium that protects them are very thin and are exposed to injuries. The most often compression of the nerve is created by the ligament, tendon or the bone itself.When pressure on the nerve exists long enough, we have neuropathy, pain, loss of sensibility…
Multiple level nerve compression can be observed sometimes up to exit from spinal cord and final branches for motor function and sensibility.
During clinical examination it can be suspected certain compression, but it is almost always necessary additional diagnostic, neurologic and electromyographic.
Pinched foot nerve treatment
Non operative treatment is usually with medicament therapy and in form of physical therapy, and depending on the level of compression surgical treatment will be considered so that nerve involved is freed, decompressed and transpositioned.
Foot and ankle bone injuries
Ankle is made of three bones: lower edges of tibia and fibula, bones of the shin and talus. Most often injuries of the ankle are in the lower part of the bones of the shin. Mechanism of the injury is mainly distorted, sprained, when forces exceed elasticity of the bones.
Depending on the type of ankle fracture, age of the patient, injury of soft tissue in the ankle region (ligament), activity and patient’s request, it is decided about the type of the treatment.
Non operative treatment usually means wearing gypsum plaster immobilization in certain period of time (most often between 8 – 10 weeks), and after that physical therapies are applied.
Operative treatment includes reposition of osseous fragments and osteosynthesis of the fracture as well as reconstaction of soft tissue structures, and then physical therapy.
Foot bone fractures are not so common injuries and mainly are caused by direct trauma in certain region of the foot. Most often it is consequence of the impact against hard object, fall from the height.
Non-operative treatment consists to orthopedic reposition and gypsum immobilization, while surgical treatment, as well as for ankle, consists of bone fragments reposition, osteosynthesis of fractures and reconstruction of the soft tissue structures.










