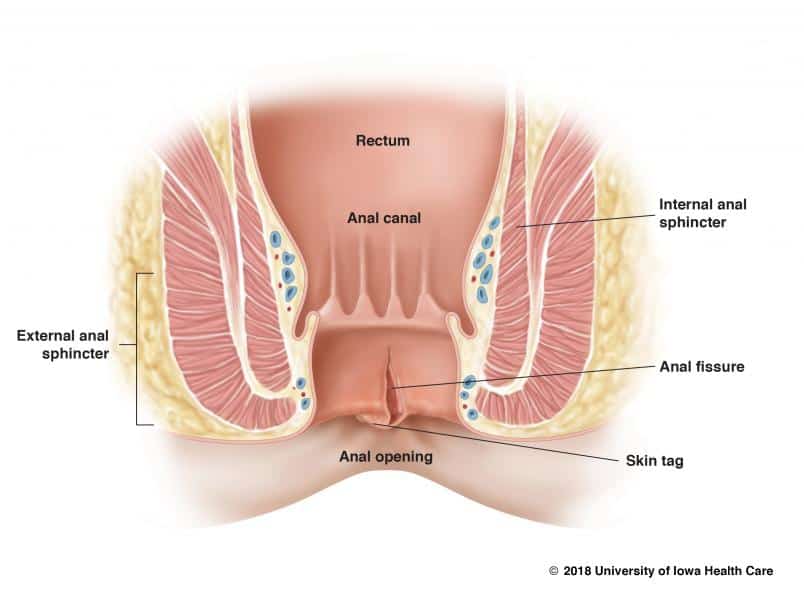
Anal canal is in the last part of the colon that goes out of the body. It is very short, length around 2.5-5 cm and has two round muscles that help in control of bowel movements. Internal anal sphincter is not voluntary muscle and is always contracted in order to prevent passing stool. External anal sphincter is voluntary muscle.
Anal fissure is damage or tear of skin of anal canal or anus trauma and anal canal. Trauma usually occurs during bowel movement or during constipation.
Acute anal fissure are shallow tear in the anoderm.
Chronic anal tear develops during time if skin tear do not heal. Damage spreads deeper in mucus or tissue that directs the muscle of internal anal sphincter.
Symptoms of anal fissure
Serious pain during bowel movement followed by continuous pain is classical symptom of anal fissure. There is cycle of constipation that causes pain that make anal sphincter muscles go into spasm. This causes more pain and spams, which makes bowel movements more difficult and makes constipation worse. Pain is significant so it could make sitting more painful.
Also, there could be several drops of light red blood on toilet paper, but major bleeding do not usually occur.
Blood in stool is never normal and any kind of bleeding should be alarm to make a visit to a doctor. Bleeding of anal fissure is minimal, and blood is not mixed with the stool.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of anal fissure is most often performed when doctor speaks with the patient and make physical examination. History of constipation followed by painful bowel movements and rectal bleeding that reoccurs are more than enough to make preliminary diagnosis.
Physical examination is usually limited on rectal examination in order to find the fissure on the anus skin. Due to pain and discomfort, rectal examination where doctor inserts finger in rectum due to abnormality examination, is usually delayed.
If fissure is not visible and there is doubt in the diagnosis itself, it could be considered a flexible sigmoidoscopy, where doctor inserts short lighted tube in the anus for the examination of the area. Usually lidocaine ointments are used in order to make procedure less unpleasant.
Usually there is no need for further blood tests or X ray.
Anal fissure treatment
Initial treatments for anal fissure that are usually successful, disagned to make the stool, enable its more easy passing and to prevent constipation. More liquids and diet that is rich in fiber are the first step, with usage of stool softener. Sometimes laxatives can be used for better bowel movements, but they should not be used on long term.
Another approach includes increasing of spasm of anal sphincter. Sitting baths (sitting in bathtub with hot water) enables muscles to relax. Different ointments are also available.
Anal fissure surgery
Surgery is another option for anal fissure. Indications for surgery are chronic anal fissure and potentially acute fissures that can not solve by itself one month after aggressive treatment. Lateral internal sphincterotomy describes procedure in which internal muscle thickened is dented in order to enable its relaxing, and with relaxing of circle inner muscle it is enabled for fissure to heal. Surgery is usually performed under general or spinal anesthesia.
Sometimes when there is chronic anal fissure, surgeon can choose to cut the fissure at the same time.
Post operative course
Pain that occurs due to fissure almost immediately vanishes after the operation. Laxatives and stool softeners can be taken several days after the operation. Diet with high fibre is usually recommendation for life time in order to prevent this kind of problem.
Medical therapy works in more than 80% of cases, as for treatment as for prevention of future anal fissure. In surgical intervention success is often more then 95 % in directive prevention.
Length of stay at the hospital after anal fissure surgery depends on the way the procedure was done, and that information will be given to the patient before the intervention.
In center for colorectal surgery of Atlas General Hospital many experts among whom are: dr Dragomir Mirković, ass dr sci med Slavenko Ostojić.
For all additional information you can call call center of Atlas General Hospital: +381 11 785 88 88.
